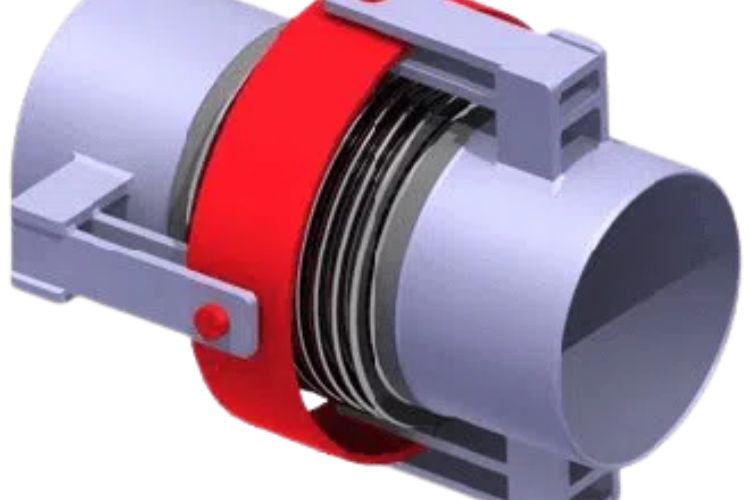
Gimbal expansion joints rarely get the spotlight, yet they quietly protect pipelines from massive stress and failure. Ever wondered what separates a reliable joint from one that causes constant maintenance headaches? The answer usually lies in design standards. Experienced manufacturers follow strict engineering principles to ensure safety, longevity, and predictable movement especially in demanding industrial environments.
When choosing a gimbal expansion joints manufacturer, understanding these standards helps buyers ask better questions and avoid costly oversights later.
Why Design Standards Matter More Than You Think?
A gimbal expansion joint isn’t just a flexible connector. It’s a load-bearing safety component designed to absorb angular movement while restraining pressure thrust. One minor miscalculation—wall thickness, hinge alignment, or material grade can compromise the entire piping system.
That’s why globally accepted standards exist. They don’t restrict innovation; they create a reliable baseline that engineers can trust across industries like power, oil & gas, petrochemicals, and steel plants.
Core Design Standards Followed by Manufacturers
1. EJMA Guidelines for Expansion Joints
Most reputable manufacturers design gimbal joints in line with recommendations from the Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association (EJMA). These guidelines define:
- Bellows geometry and convolution design
- Allowable movement ranges
- Pressure ratings and fatigue life calculations
EJMA doesn’t dictate materials or fabrication methods gimbal expansion joints manufacturer
but it ensures performance predictability under real operating conditions. According to EJMA technical publications, properly designed joints significantly reduce unplanned shutdowns (ejma.org).
2. Pressure Thrust and Structural Integrity
A defining feature of gimbal joints is their ability to restrain pressure thrust. Manufacturers carefully design:
- Gimbal rings for axial load resistance
- Hinges aligned to prevent torsion
- Pin materials that withstand cyclic stress
This is where experienced suppliers especially a gimbal expansion joints manufacturer in India working on global projects—apply both standards and real-world lessons.
3. Material Selection Based on Application
There’s no “one-size-fits-all” alloy. Design standards guide material choice based on:
- Operating temperature and pressure
- Corrosive media exposure
- Fatigue cycles over system life
Carbon steel, stainless steel, or high-nickel alloys are selected not for cost alone, but for predictable performance. This is a hallmark of a responsible gimbal expansion bellows manufacturer.
Design Verification and Testing Standards
Good design doesn’t stop at calculations. Most standards-driven manufacturers insist on verification through:
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- Hydrostatic and leak testing
- Visual and dimensional inspection
Studies published by engineering institutions such as ASME show that validated designs reduce failure risks by over 30% in high-pressure piping systems (asme.org).
Custom Engineering Within Standard Frameworks
Standards don’t limit customization they enable it. Complex piping layouts often require tailor-made solutions, guided by proven rules. Concepts like those discussed in Custom Solutions for Complex Pipe Movement: Smart Supports highlight how intelligent design adapts standards to real challenges.
Manufacturers like Flexpert Bellows apply these principles to balance flexibility, strength, and long-term reliability without overengineering.
Common Design Pitfalls Standards Help Avoid
- Underrated hinge components leading to fatigue cracks
- Improper bellows length causing movement restriction
- Ignoring thermal growth during startup conditions
Standards exist because these mistakes have already been made—and learned from—across decades of industrial operation.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of gimbal expansion joints?
They absorb angular movement while restraining pressure thrust in piping systems, protecting equipment from stress and misalignment.
2. Are EJMA standards mandatory?
They are not legally mandatory but are widely accepted as best practice across global engineering projects.
3. How do manufacturers ensure long fatigue life?
Through proper convolution design, material selection, and fatigue cycle calculations validated by testing.
4. Can gimbal joints be customized?
Yes. Most manufacturers customize size, materials, and hinge design while still following core engineering standards.
Final Thoughts
Design standards are the invisible framework holding gimbal expansion joints together literally. They translate theory into predictable, safe performance. When manufacturers respect these principles, end users gain reliability, safety, and peace of mind. In critical piping systems, that consistency is worth far more than shortcuts.